Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
10-kVA grid following converter, dc-bus voltage control#
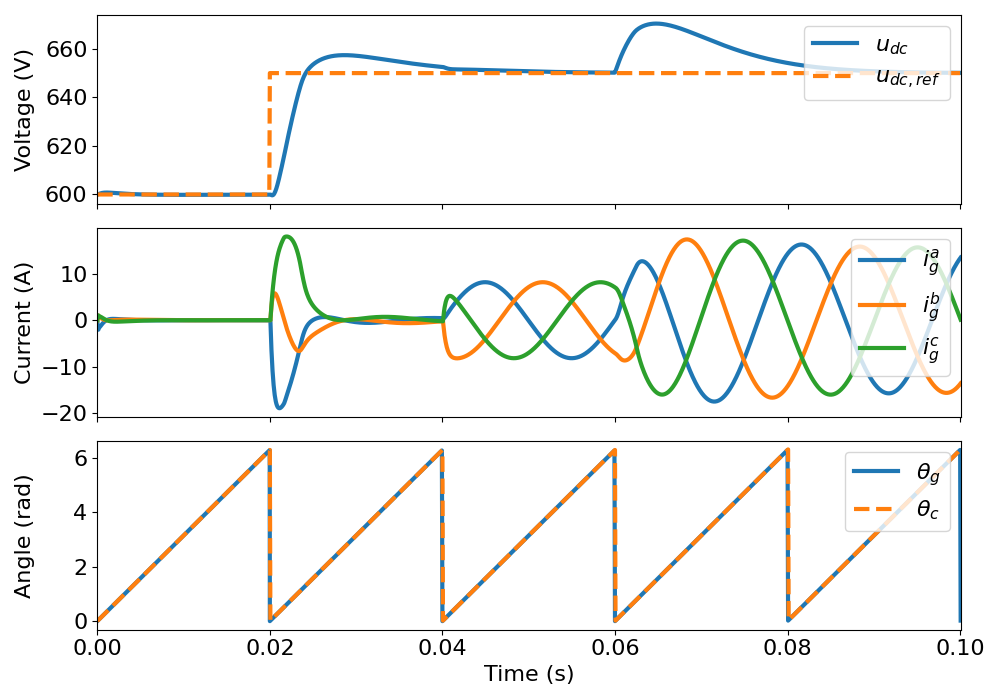
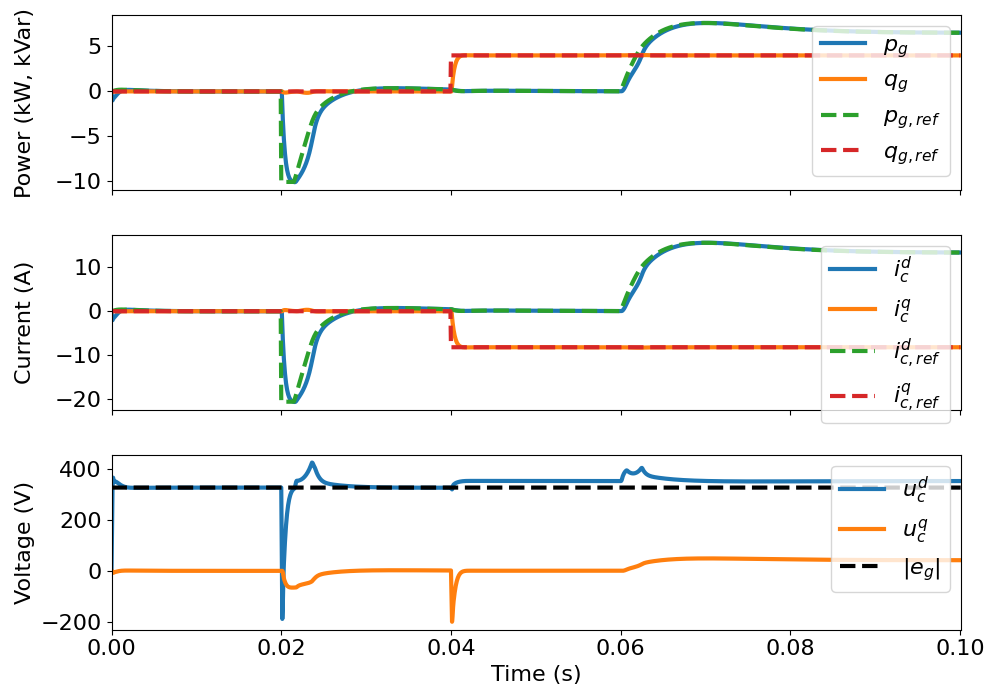
This example simulates a grid following controlled converter connected to a strong grid and regulating the dc-bus voltage at the same time. The control system includes a DC-bus voltage controller, a phase-locked loop (PLL) to synchronize with the grid, a current reference generatior and a PI-based current controller.
Imports.
import numpy as np
from gritulator import model, control
from gritulator import BaseValuesElectrical, plot_grid
# To check the computation time of the program
import time
start_time = time.time()
Compute base values based on the nominal values (just for figures).
base_values = BaseValuesElectrical(
U_nom=400, I_nom=14.5, f_nom=50.0, P_nom=10e3)
Create the system model.
# grid impedance and filter model
grid_filter = model.LFilter(L_f=10e-3, L_g=0, R_g=0)
# AC grid model (either constant frequency or dynamic electromechanical model)
grid_model = model.StiffSource(w_N=2*np.pi*50)
# DC-bus dynamic model
dc_model = model.dc_bus.DCBus(C_dc = 1e-3, u_dc0=600, G_dc=0)
converter = model.Inverter(u_dc=600)
# if you do not want to simulate any DC bus dynamics, you should define:
# dc_model = None
# This would make the DC voltage constant, using the value given from the
# converter model. Do not forget to deactivate the dc-bus control in this case.
if dc_model == None:
mdl = model.ac_grid.StiffSourceAndLFilterModel(
grid_filter, grid_model, converter)
else:
mdl = model.dc_bus.DCBusAndLFilterModel(
grid_filter, grid_model, dc_model, converter)
Configure the control system.
# Control parameters
pars = control.grid_following.GridFollowingCtrlPars(
L_f=10e-3,
C_dc = 1e-3,
f_sw = 8e3,
T_s = 1/(16e3),
on_v_dc=True,
i_max = 1.5*base_values.i,
p_max = base_values.p,
)
ctrl = control.grid_following.GridFollowingCtrl(pars)
Set the time-dependent reference and disturbance signals.
# Set the reactive power reference
ctrl.q_g_ref = lambda t: (t > .04)*(4e3)
# DC-bus external current disturbance
if dc_model != None:
mdl.dc_model.i_ext = lambda t: (t > .06)*(10)
# AC-voltage magnitude (to simulate voltage dips or short-circuits)
e_g_abs_var = lambda t: np.sqrt(2/3)*400
mdl.grid_model.e_g_abs = e_g_abs_var # grid voltage magnitude
# DC voltage reference
ctrl.u_dc_ref = lambda t: 600 + (t > .02)*(50)
Create the simulation object and simulate it.
sim = model.Simulation(mdl, ctrl, pwm=False)
sim.simulate(t_stop = .1)
# Print the execution time
print('\nExecution time: {:.2f} s'.format((time.time() - start_time)))
Execution time: 0.98 s
Plot results in SI or per unit values.
plot_grid(sim, base=None)
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 1.600 seconds)