Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
10-kVA converter#
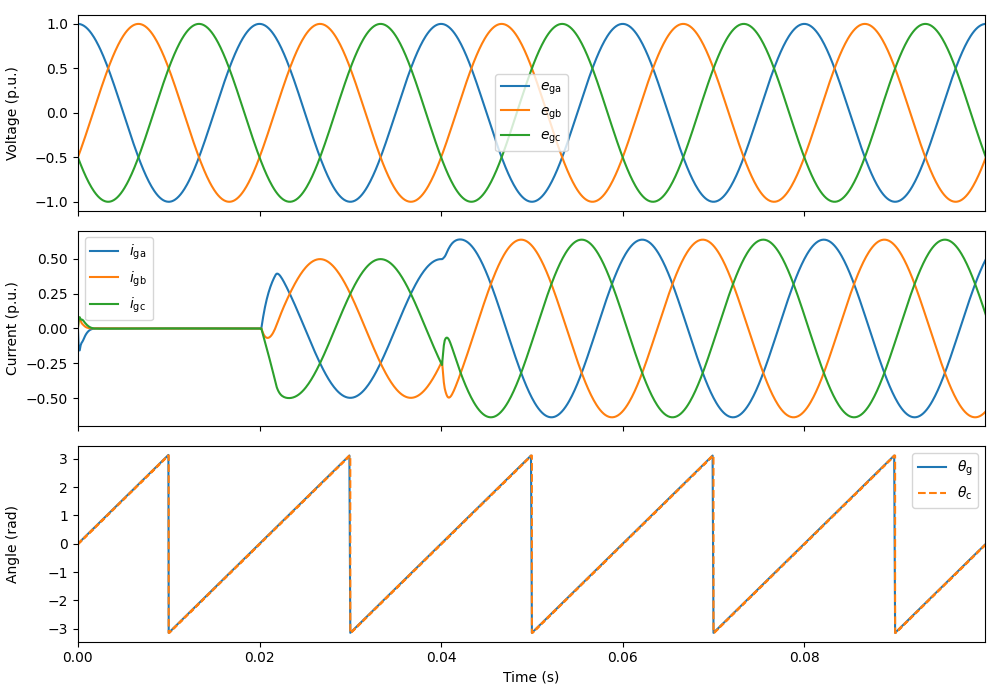
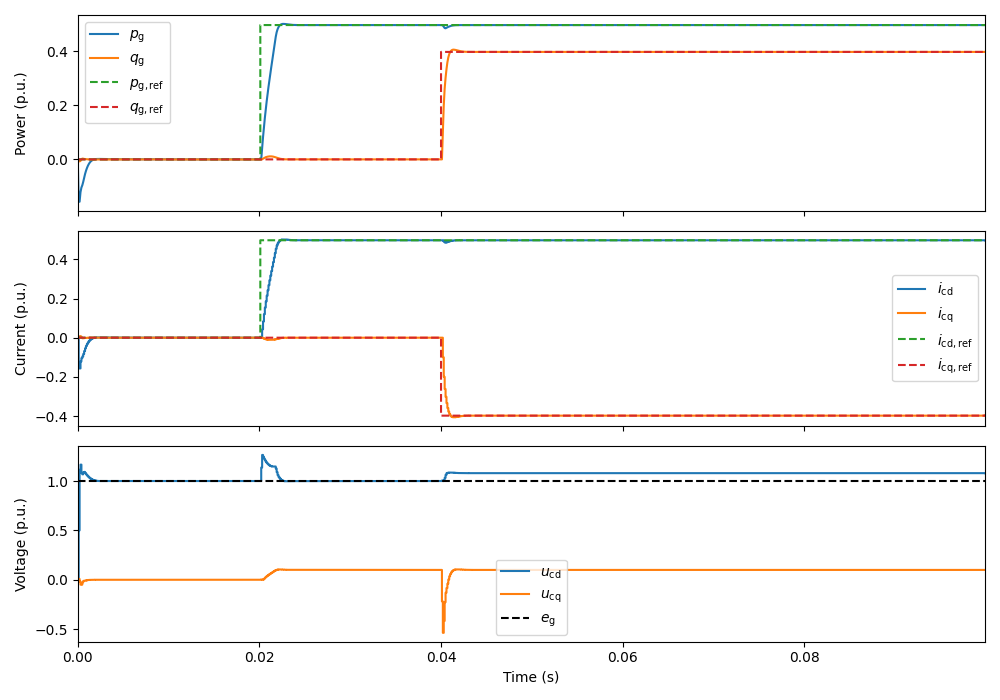
This example simulates a grid-following-controlled converter connected to a strong grid. The control system includes a phase-locked loop (PLL) to synchronize with the grid, a current reference generator, and a PI-based current controller.
from motulator.common.model import VoltageSourceConverter, Simulation
from motulator.common.utils import BaseValues, NominalValues
from motulator.grid import model
import motulator.grid.control.grid_following as control
from motulator.grid.utils import FilterPars, GridPars, plot
# from motulator.grid.utils import plot_voltage_vector
# from motulator.common.model import CarrierComparison
# import numpy as np
Compute base values based on the nominal values.
nom = NominalValues(U=400, I=14.5, f=50, P=10e3)
base = BaseValues.from_nominal(nom)
Configure the system model.
# Grid parameters
grid_par = GridPars(u_gN=base.u, w_gN=base.w)
# Filter parameters
filter_par = FilterPars(L_fc=.2*base.L)
# Create AC filter with given parameters
ac_filter = model.ACFilter(filter_par, grid_par)
# AC grid model with constant voltage magnitude and frequency
grid_model = model.ThreePhaseVoltageSource(w_g=base.w, abs_e_g=base.u)
# Inverter with constant DC voltage
converter = VoltageSourceConverter(u_dc=650)
# Create system model
mdl = model.GridConverterSystem(converter, ac_filter, grid_model)
# Uncomment line below to enable the PWM model
# mdl.pwm = CarrierComparison()
Configure the control system.
# Control configuration parameters
cfg = control.GFLControlCfg(grid_par, filter_par, max_i=1.5*base.i)
# Create the control system
ctrl = control.GFLControl(cfg)
Set the time-dependent reference and disturbance signals.
# Set the active and reactive power references
ctrl.ref.p_g = lambda t: (t > .02)*5e3
ctrl.ref.q_g = lambda t: (t > .04)*4e3
# Uncomment lines below to simulate a unbalanced fault (add negative sequence)
# mdl.grid_model.par.abs_e_g = .75*base.u
# mdl.grid_model.par.abs_e_g_neg = .25*base.u
# mdl.grid_model.par.phi_neg = -np.pi/3
Create the simulation object and simulate it.
sim = Simulation(mdl, ctrl)
sim.simulate(t_stop=.1)
Plot the results.
# By default results are plotted in per-unit values. By omitting the argument
# `base` you can plot the results in SI units.
# Uncomment line below to plot locus of the grid voltage space vector
# plot_voltage_vector(sim, base)
plot(sim, base, plot_pcc_voltage=False)
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 1.296 seconds)