Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
12.5-kVA converter, RFPSC#
This example simulates reference-feedforward power-synchronization control (RFPSC) of a converter connected to a weak grid.
from motulator.common.model import VoltageSourceConverter, Simulation
from motulator.common.utils import BaseValues, NominalValues
from motulator.grid import model
import motulator.grid.control.grid_forming as control
from motulator.grid.utils import FilterPars, GridPars, plot
Compute base values based on the nominal values.
nom = NominalValues(U=400, I=18, f=50, P=12.5e3)
base = BaseValues.from_nominal(nom)
Configure the system model.
# Grid parameters
grid_par = GridPars(u_gN=base.u, w_gN=base.w, L_g=.74*base.L)
# Uncomment line below to simulate a strong grid
# grid_par.L_g = 0
# Filter parameters
filter_par = FilterPars(L_fc=.15*base.L)
# Create AC filter with given parameters
ac_filter = model.ACFilter(filter_par, grid_par)
# Grid voltage source with constant frequency and voltage magnitude
grid_model = model.ThreePhaseVoltageSource(w_g=base.w, abs_e_g=base.u)
# Inverter with constant DC voltage
converter = VoltageSourceConverter(u_dc=650)
# Create system model
mdl = model.GridConverterSystem(converter, ac_filter, grid_model)
Configure the control system.
# Control configuration parameters
cfg = control.RFPSCControlCfg(
grid_par, filter_par, max_i=1.3*base.i, T_s=100e-6, R_a=.2*base.Z)
# Create the control system
ctrl = control.RFPSCControl(cfg)
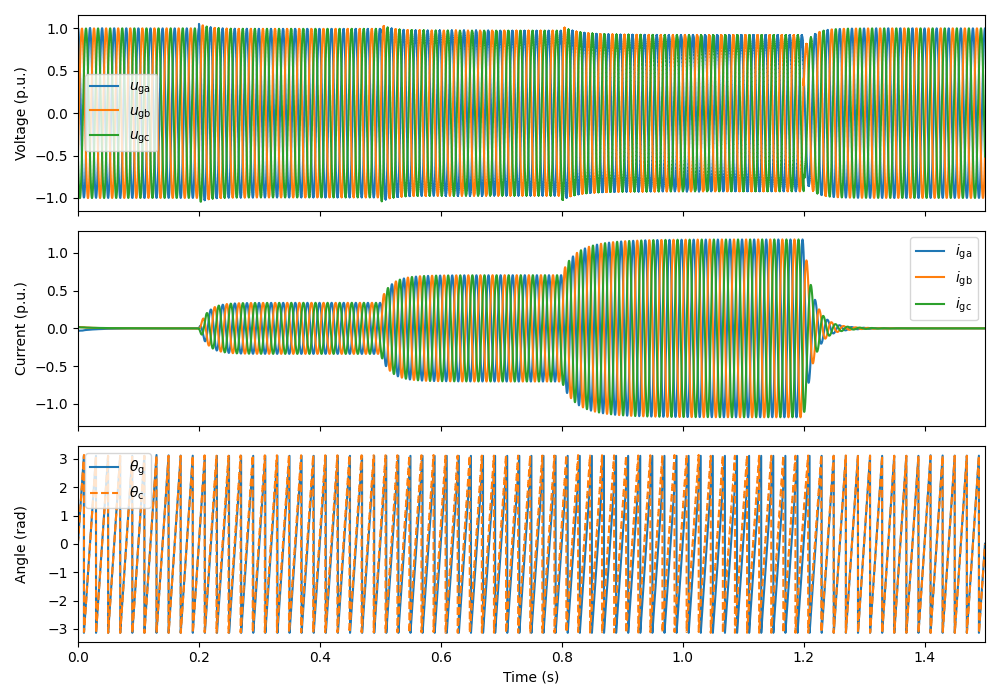
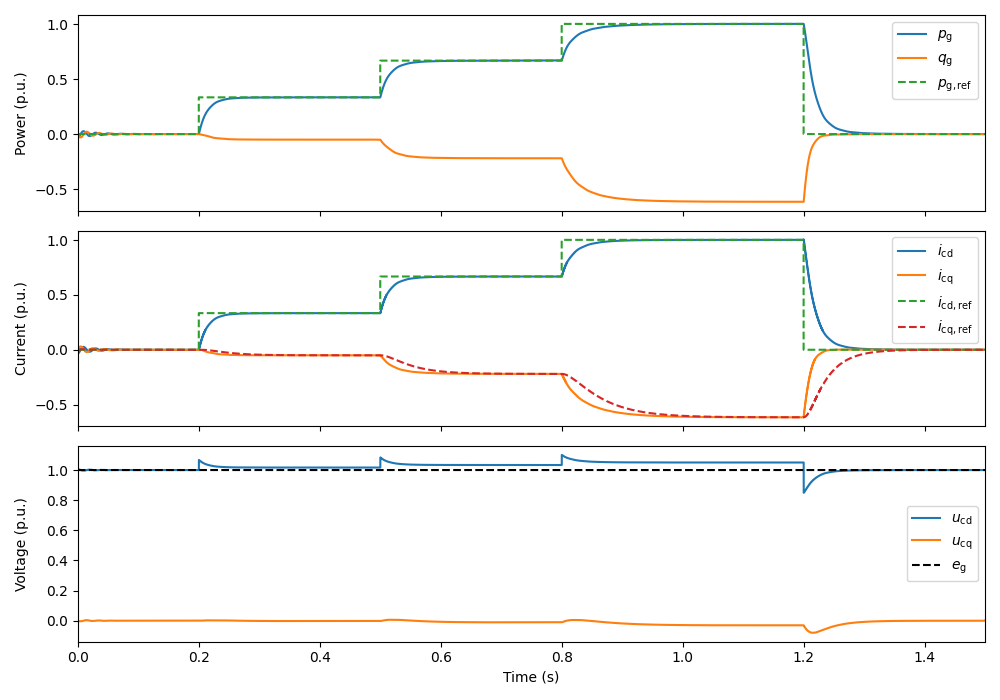
Set the references for converter output voltage magnitude and active power.
# Converter output voltage magnitude reference
ctrl.ref.v_c = lambda t: base.u
# Active power reference
ctrl.ref.p_g = lambda t: ((t > .2)/3 + (t > .5)/3 + (t > .8)/3 -
(t > 1.2))*nom.P
Create the simulation object and simulate it.
sim = Simulation(mdl, ctrl)
sim.simulate(t_stop=1.5)
Plot the results.
plot(sim, base)
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 8.216 seconds)