Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
10-kVA converter, DC-bus voltage#
This example simulates a grid-following-controlled converter connected to a strong grid and regulating the DC-bus voltage. The control system includes a DC-bus voltage controller, a phase-locked loop (PLL) to synchronize with the grid, a current reference generator, and a PI-type current controller.
import numpy as np
from motulator.grid import control, model, utils
Compute base values based on the nominal values.
nom = utils.NominalValues(U=400, I=14.5, f=50, P=10e3)
base = utils.BaseValues.from_nominal(nom)
Configure the system model.
ac_filter = model.LFilter(L_f=0.2 * base.L)
ac_source = model.ThreePhaseSource(w_g=base.w, e_g=base.u)
converter = model.CapacitiveDCBusConverter(u_dc=600, C_dc=1e-3)
mdl = model.GridConverterSystem(converter, ac_filter, ac_source)
Configure the control system.
dc_bus_voltage_ctrl = control.DCBusVoltageController(
C_dc=1e-3, alpha_dc=2 * np.pi * 30, p_max=base.p
)
inner_ctrl = control.CurrentVectorController(i_max=1.5 * base.i, L=0.2 * base.L)
ctrl = control.GridConverterControlSystem(inner_ctrl, dc_bus_voltage_ctrl)
Set the time-dependent reference and disturbance signals.
# Set the references for DC-bus voltage and reactive power
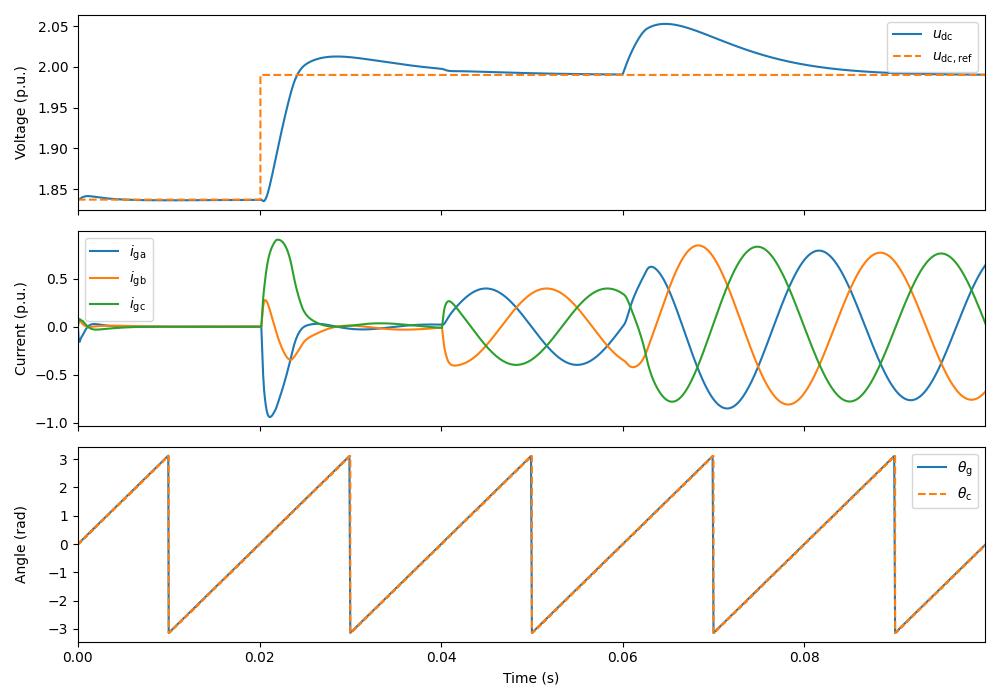
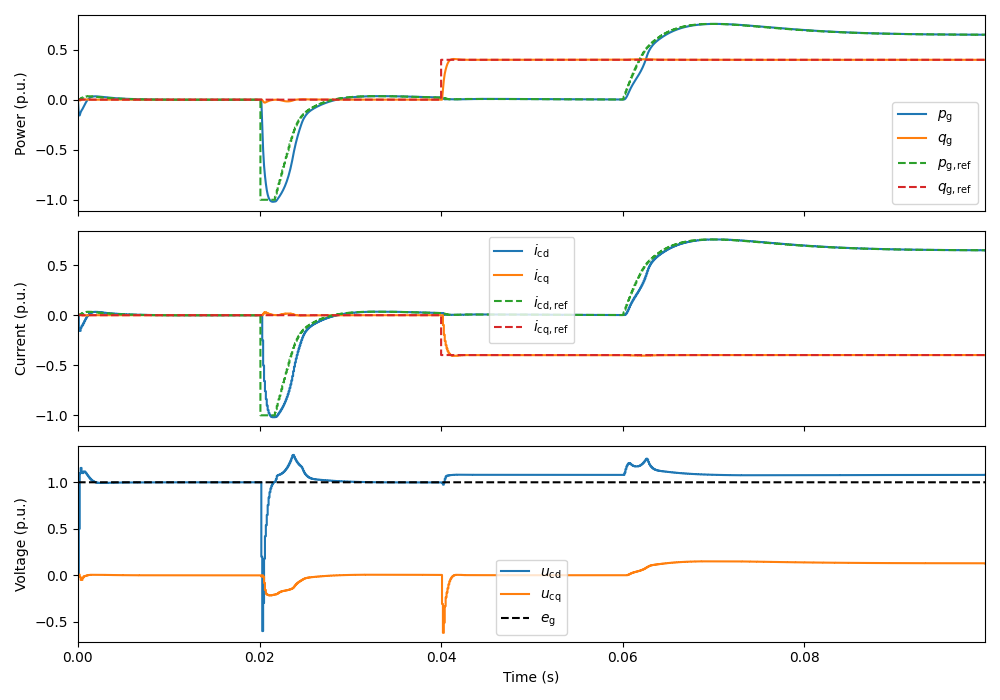
ctrl.set_dc_bus_voltage_ref(lambda t: 600 + (t > 0.02) * 50)
ctrl.set_reactive_power_ref(lambda t: (t > 0.04) * 4e3)
# Set the external current fed to the DC bus
mdl.converter.set_external_dc_current(lambda t: (t > 0.06) * 10)
Create the simulation object, simulate, and plot the results in per-unit values.
sim = model.Simulation(mdl, ctrl)
res = sim.simulate(t_stop=0.1)
utils.plot_control_signals(res, base)
utils.plot_grid_waveforms(res, base)
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 1.058 seconds)