Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
2.2-kW IM, CVC, torque-control mode#
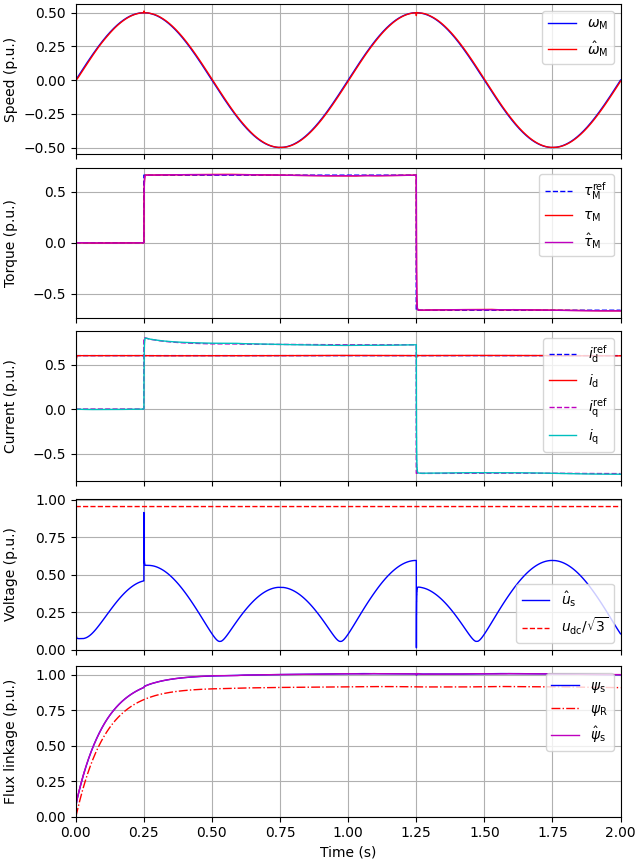
This example simulates current-vector control (CVC) of a 2.2-kW induction motor (IM) drive in torque-control mode.
Compute base values based on the nominal values.
nom = utils.NominalValues(U=400, I=5, f=50, P=2.2e3, tau=14.6)
base = utils.BaseValues.from_nominal(nom, n_p=2)
Configure the system model.
# Parametrize the machine model using its inverse-Γ parameters
par = model.InductionMachineInvGammaPars(
n_p=2, R_s=3.7, R_R=2.1, L_sgm=0.021, L_M=0.224
)
machine = model.InductionMachine(par)
mechanics = model.ExternalRotorSpeed()
converter = model.VoltageSourceConverter(u_dc=540)
mdl = model.Drive(machine, mechanics, converter)
Configure the control system.
est_par = control.InductionMachineInvGammaPars(
n_p=2, R_s=3.7, R_R=2.1, L_sgm=0.021, L_M=0.224
)
cfg = control.CurrentVectorControllerCfg(psi_s_nom=base.psi, i_s_max=1.5 * base.i)
vector_ctrl = control.CurrentVectorController(est_par, cfg, sensorless=True)
ctrl = control.VectorControlSystem(vector_ctrl, speed_ctrl=None)
Set the torque reference and the actual speed.
Create the simulation object, simulate, and plot the results in per-unit values.
sim = model.Simulation(mdl, ctrl)
res = sim.simulate(t_stop=2)
utils.plot(res, base)
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 6.282 seconds)